GenTegra’s Proprietary ACP Coating Protects Biomolecules Ensuring High Quality Samples and More Accurate Analytical Results
Purified and unprotected DNA
PLUS
Active Chemical Protection
ACP Protected DNA
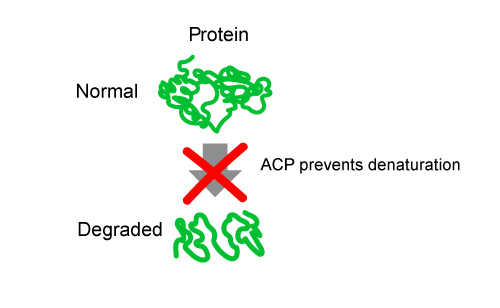
- GenTegra ACP protects biomolecules, e.g. DNA & RNA, from exposure to the environment heat, oxygen), nucleases, and proteases, which can damage and degrade the biomolecules.
- The GenTegra ACP coating action acts as a shield against all forms of degradation and denaturization, which keeps the biomolecules stable and protected.
- ACP is available in multiple formulas and formats (simple chemical matrix, on different carrier matrix like paper and others) to protect biomolecules, in a wide variety of applications.
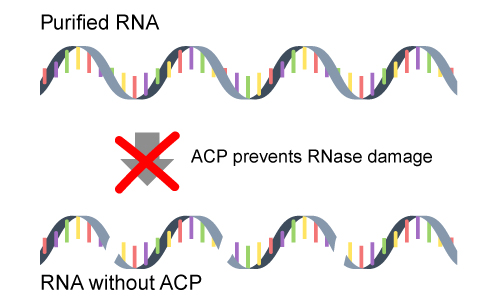
Better RNAseq results
GenTegra’s Active Chemical Protection formulation provides unparalleled stability and shielding of purified RNA samples from degradation. GenTegra RNA keeps RNA stable during shipping without dry ice. Ambient shipping reduces the risk of sample loss, improves the quality of RNAseq results, and reduces overall costs.
Patient Centric Sampling
The evolution taking place in micro-sample blood collection devices is driving the creation of an entirely new paradigm in patient-centered medicine. Improved patient compliance and convenience are some of the many benefits of these new devices. GenTegra’s Active Chemical Protection technology will play a critical role to ensure the quality of samples collected and analyzed for routine clinical care and pharmaceutical clinical trials.
Coroner & Forensic Field Samples
Remote field-based collection and shipment of samples to the laboratory presents unique challenges. GenTegra’s suite of field collection card products, utilizing Active Chemical Protection technology protect DNA, RNA and small molecule samples from the hazards of environmental degradation during shipment or long-term storage.
Biobanking
GenTegra dry ambient storage technology vs. traditional freezer storage represents significant savings in cost savings, space efficiency, and lower risk of sample loss.